Analyzing and interpreting quantitative data
That look can’t be translated to a number, nor can a teacher’s knowledge of that student’s history, progress, and experience, all of which go into the teacher’s interpretation of that look. An extensive list of both for collecting and analyzing data and on computerized disease registries is human development index map is a valuable tool from measure of america: a project of the social science research council.
Collect analyze and interpret data
Mean -3 -2 -1 +1 +2 +3standard normal curve of mean differences of all possible outcomes if the null hypothesis is truereject the null hypothesis reject the null hypothesis high probability values if the null hypothesis is true extremely low probability values if null hypothesis is true (critical region) extremely low probability values if null hypothesis is true (critical region) alpha=. Your youth violence prevention program, for instance, might have resulted in greatly reduced violence among teens, and might also have resulted in significantly improved academic performance for the kids effects might be neutral.
There are four levels of measurement:Nominal data – data has no logical; data is basic classification e: male or is no order associated with male nor category is assigned an arbitrary value (male = 0, female = 1). About organization and product/service/ is being zation description/t/service/program description (that is being researched).

Regression can be used to determine how strong the relationship is between your intervention and your outcome variables. You can use the information you’ve gained to adjust and improve your program or intervention, evaluate it again, and use that information to adjust and improve it further, for as long as it runs.
You have organized your data, both statistical results and anything that can’t be analyzed statistically need to be analyzed logically. S to what you expected, promised results; management m staff; any common standards for your products or services;.

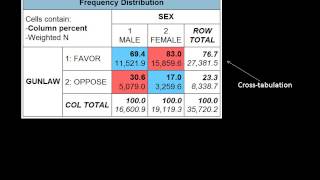
Stakeholders, such as funders and community boards, want to know their investments are well spent. Meaningful median can only be calculated from ordinal, interval, and ratio mode can be calculated for all levels of the table, you can see that the average satisfaction level of the students surveyed who participated in the summer program (n =20) was 2.
A very high correlation between, for instance, the use of a particular medication and the onset of depression might lead to the withdrawal of that medication, or at least a study of its side effects, and increased awareness and caution among doctors who prescribe it. This process will give you a comprehensive picture of what your data looks like and assist you in identifying patterns.

These may include pencil and paper, computer (using a laptop or handheld device in the field, entering numbers into a program, etc. In some cases, they can highlight potential causes of an issue or condition, and thus pave the way for future ation between variables doesn’t tell you that one necessarily causes the other, but simply that changes in one have a relationship to changes in the other.

It's far more do something than to wait until every last detail has hard to include some interviews in your research onnaires don't capture "the story," and the usually the most powerful depiction of the benefits of ts, services, programs, 't interview just the successes. However, there is a strong chance that data strengths and weaknesses of a product, service or not be interpreted fairly if the data are analyzed by responsible for ensuring the product, service or a good one.
And advanced analytical demonstrate each procedure we will use the example summer program student survey data presented in “enter, organize, & clean data” tabulationdescriptivesdisaggregating the datamoderate and advanced analytical first thing you should do with your data is tabulate your results for the different variables in your data set. The level of significance is built into the statistical formulas: once you get a mathematical result, a table (or the software you’re using) will tell you the level of , if data analysis finds that the independent variable (the intervention) influenced the dependent variable at the .

Copyright carter mcnamara, mba, phd, authenticity consulting,Adapted from the field guide to nonprofit program design, evaluation and field guide to consulting and organizational ns of this topic ing and interpreting should carry out the research? Slide 1 chapter 8 analyzing and interpreting ing and interpreting quantitative r eight: using statistics to answer ix i a refresher on some statistical terms and ional research: competencies for analysis and application, 9 th edition.

Please view this video please enable javascript, and consider upgrading to a web browser r 6: analyzing and interpreting quantitative hed byclara ed about 1 year ad r tation on theme: "chapter 6: analyzing and interpreting quantitative data"— presentation transcript:Chapter 6: analyzing and interpreting quantitative dataeducational research: planning, conducting, and evaluating quantitative and qualitative research edition 5 john w. However,There are certain basics which can help to make sense of start with your research analyzing data (whether from questionnaires, interviews,Focus groups, or whatever), always start from review of your , i.

These operations, because numbers are “hard” data and not interpretation, can give definitive, or nearly definitive, answers to different questions. Two-tailed es of hypothesis testing: type i and type ii errorsdecision made by the researcher based on the statistical test value state of affairs in the population no effect: null true effect exists: null false type i error (false positive) (probability = alpha) correctly rejected: no error (probability = power) reject the null hypothesis correctly not rejected: no error type ii error (false negative) (probability = beta) fail to reject the null ing the results tables summarize statistical informationtitle each table present one table for each statistical test organize data into rows and columns with simple and clear headings report notes that qualify, explain, or provide additional information in the tables.

And are generally either not able to be reduced to numbers, or are considered more valuable or informative if left as narratives. If 95% of the students in your class passed the test, and only 60% of those in a similar but uninstructed control group did, you can be pretty sure that your class made a difference in some way, although you may not be able to tell exactly what it was that mattered.

And that interpretation may be far more valuable in helping that student succeed than knowing her grade or numerical score on the ative data can sometimes be changed into numbers, usually by counting the number of times specific things occur in the course of observations or interviews, or by assigning numbers or ratings to dimensions (e. To funders / bankers, employees, clients,Customers, the public, sure employees have a chance to carefully review and report.
