John dewey critical thinking
From the work of piaget, we have increased our awareness of the egocentric and sociocentric tendencies of human thought and of the special need to develop critical thought which is able to reason within multiple standpoints, and to be raised to the level of "conscious realization. Dewey defined critical thinking as “reflective thought,” requiring healthy skepticism, an open mind, and suspended judgment. Thus, dewey argued, the schools did not provide genuine learning experiences but only an endless amassing of facts, which were fed to the students, who gave them back and soon forgot distinguished between the psychological and the logical organization of subject matter by comparing the learner to an explorer who maps an unknown territory.
Self-directed thinking which exemplifies the perfection of thinking appropriate to a particular mode or domain of thinking (paul, 1989, p. And critical thinking is significant in the learning process of application, whereby those ideas, principles, and theories are implemented effectively as they become relevant in learners' discipline adapts its use of critical thinking concepts and principles. Because the salary offer was quite low for a man with six children (three more had been born during his ten years at chicago), arrangements were made for dewey to teach an additional two hours a week at columbia teachers college for extra compensation.

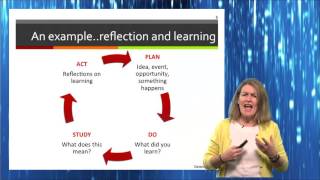
Rs should model metacognitive and gies on specific problems to help students build an tanding of the process of guides or advance organizer integrated into classroom materials to prompt students to reflect oning strategies should be used reflective thinking, specifically getting students to respond , how, and what specific decisions ng environments should exist that orative work with peers, teachers, and be designed to include advice from teachers be relevant to real-world situations and provide oom experiences should involve enjoyable, concrete,And physical learning activities whenever possible to ensure ion to the unique cognitive, affective, and psychomotor pment of middle school t reflective thinking? Such an example illustrates all the elements of dewey's theoretical description of reflective thinking: a real problem arises out of present experiences, suggestions for a solution come to mind, relevant data are observed, and a hypothesis is formed, acted upon, and finally dewey, learning was primarily an activity which arises from the personal experience of grappling with a problem. Good thinking, he argues, embraces contradiction rather than shunning it:Concentration does not mean fixity, nor a cramped arrest or paralysis of the flow of suggestion.
- hausarbeit schreiben lernen
- term paper writer review
- defination of research proposal
- creative cursive writing

The educator and psychologist john dewey first used the phrase in its modern sense in his 1910 book how we think, though there are instances of the words appearing together in texts before this time. With this taste of success and a $500 loan from his aunt, dewey left teaching to do graduate work at johns hopkins university. The declaration of principles on tolerance adopted by unesco in 1995 affirms that "education for tolerance could aim at countering factors that lead to fear and exclusion of others, and could help young people to develop capacities for independent judgement, critical thinking and ethical reasoning.
- what is an ethical statement
- criminal law research paper
- cheap paper writing service
- concept of business plan

To dismiss experiences and ideas in that way is, then, a profound failure of reflective thinking and of our highest human potentiality. A content analysis method to measure critical thinking in face-to-face and computer supported group learning". In the 20th century, our understanding of the power and nature of critical thinking has emerged in increasingly more explicit formulations.

On average, students ative learning performed at over nine-tenths a ion above their competitive learning student chie found three factors that accounted for student critical thinking competencies; (1) discussion among students,(2) explicit emphasis on problem solving methods, and (3) methods and strategies to encourage development of ative learning promotes positive attitudes towards the perhaps attracts "majors". Isbn 978-0-521-79679-8; thinking and reasoning in human decision making: the method of argument and heuristic analysis, facione and facione, 2007, california academic press. Through the use of critical thinking, nurses can question, evaluate, and reconstruct the nursing care process by challenging the established theory and practice.

At chicago he established the now-famous laboratory school (commonly known as the dewey school), where he scientifically tested, modified, and developed his psychological and educational early statement of his philosophical position in education, my pedagogic creed (1897), appeared three years after his arrival at chicago. Clearly, a person may be hampered in any of these three regards: his thinking may be irrelevant, narrow, or crude because he has not enough actual material upon which to base conclusions; or because concrete facts and raw material, even if extensive and bulky, fail to evoke suggestions easily and richly; or finally, because, even when these two conditions are fulfilled, the ideas suggested are incoherent and fantastic, rather than pertinent and stock our “store of experiences and facts” via one of the greatest human faculties — our inherent curiosity, a “desire for the fullness of experience”:The most vital and significant factor in supplying the primary material whence suggestion may issue is, without doubt, curiosity… the curious mind is constantly alert and exploring, seeking material for thought, as a vigorous and healthy body is on the qui vive for nutriment. It is this natural form of learning from experience, by doing and then reflecting on what happened, which dewey made central in his approach to tive thinking and the perception of relationships arise only in problematical situations.
- essay paper writing services
- purpose of research methodology
- human resources in business plan
- what's in a conclusion

Walters (re-thinking reason, 1994) argues that rationality demands more than just logical or traditional methods of problem solving and analysis or what he calls the "calculus of justification" but also considers "cognitive acts such as imagination, conceptual creativity, intuition and insight" (p. Criteria for making the judgment able methods or techniques for forming the able theoretical constructs for understanding the problem and the question at addition to possessing strong critical-thinking skills, one must be disposed to engage problems and decisions using those skills. Thus we view critical thinking as the emotional ability to go beyond the known without " pieces".

The lesson plans:Provide teacher questions designed to ts to identify and clarify overall and subordinate e many opportunities to engage gathering information to look for possible causes and e ideas and activity sheets to ts evaluate the evidence they e questions that prompt students er alternatives and implications of their e questions and activities that ts to draw conclusions from the evidence they gathered and e opportunities for students to implement the best age students to monitor and results and findings throughout the entire orates prompts and scaffolding suggestions to promote uring lesson plans to support ing lesson components that prompt inquiry ing resources and hand-on activities to ing reflective thinking activities that ts to think about what they have done, what they learned, they still need to ing reflection activity worksheets for plan to prompt students to think about what they know, what d, and what they need to know as they progress through ation on critical and reflective thinking:Reflective thought, critical thinking (eric digest). Smith's study indicates that increased ipation and peer interaction are correlated positively ed critical thinking scores on the watson-glaser ng appraisal and chickering critical thinking . The dull make no response; the bright flash back the fact with a changed dewey’s most prescient point has to do with how information overload — a malady undoubtedly far worse today than it was in 1910, yet one each era bemoans by its own terms — muddles the clarity of our view, hindering our ability to think critically and reflectively:So many suggestions may rise that the person is at a loss to select among them.
- defination of research proposal
- social work research papers
- social work research papers
- storage facility business plan

Assessing critical thinking in online discussion forums often employ a technique called content analysis,[36][35] where the text of online discourse (or the transcription of face-to-face discourse) is systematically coded for different kinds of statements relating to critical thinking. There is some evidence to suggest a fourth, more nuanced possibility: that cmc may promote some aspects of critical thinking but hinder others. Dewey writes:Such thoughts grow up unconsciously and without reference to the attainment of correct belief.
