Design based research
Design research: theoretical and methodological issues, the journal of the learning sciences, 13(1), -based research collective (2003) design-based research: an emerging paradigm for educational inquiry. Mentioned in the conclusion to the 2008 icls keynote([1]), there are several forms of design based research now in use in education research.

It is aimed at both researchers and educational leaders in schools, districts, and out of school settings. There was some debate in his talk wether one could organize some comparative analysis from similar projects (a bit like in political science' similar systems design).

Situation-specific knowledge is an other important feature:``a core part of design-based research as applied work involves situating the work in "naturalistic contexts". In design-based research, however, the goal is not testing not the theory works (van den akker, 1999).

Many programs require more resources and know-how than individual researchers and educators can provide to make them work for all -based implementation research (dbir) is an approach to organizing research and development intended to address these challenges. 9) and theory is ped and elaborated throughout the research process acting as a the enacted innovations (van den akker & et al.

Formative evaluation, design-based research uses mixed methods to analyze an intervention’s outcomes and refine the intervention. Edelson (2002) proposed three kinds of theories be generated from the design:Domain theories describe learning situations ts, teachers, learning environments and their n (2002) argued that theories about context and outcomes of the theories that design research generates.

Is imperative that design-based researchers ed records during the design research process concerning how outcomes (e. Based research (dbr) is a type of research methodology commonly used by researchers in the learning sciences.

In addition,Design-based research is conducted in real-world contexts replete complexities, dynamics and limitations of authentic practice. Development research, on the other hand, requires a pragmatic epistemology that regards learning theory as being collaboratively shaped by researchers and practitioners.

People engaged in these ches hope to be able to design instruction based on the the theory and associated experimental results support (edelson,2002). Design experiments entail both engineering particular forms of learning and systematically studying those forms of learning within the context defined by the means of supporting them.

The design-based research methodology is often employed by learning scientists in their inquiries because this methodological framework considers the subject of study to be a complex system involving emergent properties that arise from the interaction of more variables than are initially known to researchers, including variables stemming from the researchers themselves (brown, 1992). The overall goal of development research is to solve real problems while at the same time constructing design-principles that can inform future decisions.

The theories of traditional research are over the walls of schools and other contexts with little ement. This designed context is subject to test and revision, and the successive iterations that result play a role similar to that of systematic variation in experiment.

There are case examples, as well as specific tools and routines for organizing research and development projects that maintain integrity to the four principles of is an introduction to dbir from bill penuel and colleagues, jointly produced with the research + practice ting sustainability: teachers’ advice networks and ambitious instructional reform. It needs futher corroboration with more traditional research ing to sandoval (talk at epfl, 2007), types of knowledge that dbr typically can produce:Design knowledge (edelson, 2002).

A blend of empirical educational research with the theory-driven design of learning environments, dbr is an important methodology for understanding how, when, and why educational innovations work in practice; dbr methods aim to uncover the relationships between educational theory, designed artefact, and ators: a. Some researchers question whether design-based research is primarily useful as an exploratory research method geared towards producing designed artifacts, or whether it can validly test robust theories that are contingent on designed artifacts or ies and forms of design-based research methodologies[edit].

In press), the design-based research proposed by wang and hannafin (2005) critical characteristics:A systematic but flexible methodology aimed to ional practices through iterative analysis, design, development,And implementation, based on collaboration among researchers and real-world settings, and leading to contextually-sensitive ples and theories (p. Susan mckenney & jan herrington (2011), publishing and perishing: the critical importance of educational design research, australasian journal of educational technology, 27(1), 55-65.

Therefore,Researchers use design to enact and refine theories continuously (edelson,2002) so that the theories do real work in practice (cobb, confrey,Disessa, lehrer, and shauble, 2003, p. Design-based research is conducted is fundamentally different tory experiments that deal with a single variable, control all s and isolate subjects and situation from the real world (collins,1999; collins, joseph & bielaczyc, 2004; van den akker & et al.
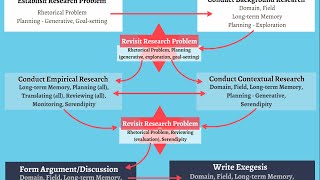
Unlike evaluation research, design-based research views a successful innovation as a joint product of the designed intervention and the context. In 1999, christopher hoadley founded the design-based research collective, funded by the spencer foundation, and coined the modern term for the -based research methodologies are often viewed as non-scientific by traditional experimental psychologists because design-based research does not follow formal definitions of scientific method.
